
About ε-Polylysine
Explain the difference between ε-Polylysine, ε-Polylysine hydrochloride, and α-Polylysine
Polylysine is a polyamino acid in which lysines, an essential amino acid, are multiply bound together. Polylysine has multiple structures: ε-Polylysine, ε-Polylysine hydrochloride, and α-Polylysine. This page will explain the features of each of Polylysine.
1. ε-Polylysine(Free form)
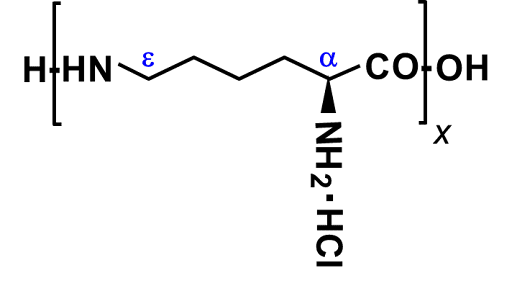
Formally it is called ε-poly-L-lysine. The essential amino acid L-lysine is peptide-bonded at the side chain amino group (ε-position) and has a unique chemical structure. The amino group at the α-position has strong cationic properties, making it a highly cationic polymer. ε-Polylysine is a free form of Polylysine which is not contain a salt as a counter ions. JNC manufactures this free-form ε-Polylysine.

ε-Polylysine has both cationic and hydrophobic properties due to the presence of four carbon (C4) between the amino groups. This structure gives it specific properties. For example, it can be selectively adsorbed endotoxin, which is the causative agent of sepsis. Taking advantage of this property, it is also used as an endotoxin adsorbent. ε-Polylysine also has cell adhesion ability, so it is also applied as a coating agent for cell culture vessels.
ε-Polylysine is approved as a food additive in Japan, South Korea and China. In Japan and South Korea, ε-Polylysine hydrochloride and α-Polylysine are not approved as food additives. In China, they are clearly distinguished between the free form and hydrochloride. The foods that can be used with each Polylysine are different, and the allowable amount of Polylysine added is also different. α-Polylysine is not recognized as a food additive in China.
ε-Polylysine (free form) manufactured by JNC has received the FDA GRAS certification in the United States. (GRN No.135, GRN No.336). This certification number applies only to ε-Polylysine manufactured by JNC Corporation. GRAS certification is subject to rigorous review not only of the substance itself, but also of the manufacturing process.
ε-Polylysine is produced by fermentation using microorganisms. JNC's ε-Polylysine (free form) is a natural food additive because it does not involve chemical synthesis even in the post-fermentation manufacturing process.
Free form ε-Polylysine is very difficult to powderization due to its high hygroscopicity. Therefore, JNC manufactures 25% aqueous solution and 50% powder which contains 50% dextrin as an excipient. 100% ε-Polylysine free form powder is difficult to produce industrially. Most of the powders which concentration are 90% or more ε-Polylysine are hydrochloride types.
2. ε-Polylysine hydrochloride
ε-Polylysine hydrochloride cannot be said to be a pure natural material because the salt-forming reaction during its manufacturing process corresponds to the chemical synthesis process. Hydrochlorination makes ε-Polylysine easier to powder. Most commercially available high-concentration ε-Polylysine powder products are hydrochloride type.
ε-Polylysine hydrochloride easily dissociates from ε-Polylysine into chloride ions in an aqueous solution. Chloride ions can accelerate corrosion of metals. There is concern that such corrosion may affect manufacturing equipment and food processing lines.
3. α-Polylysine
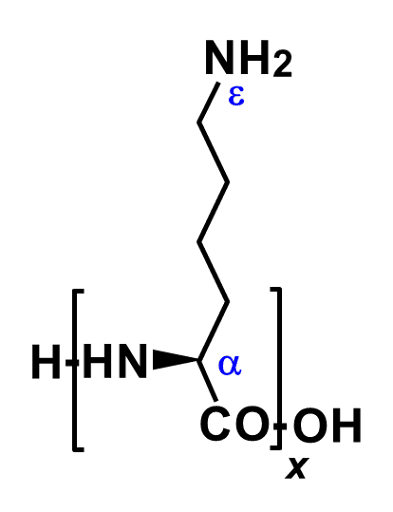
α-Polylysine is a polymer that the amino group of α-amino position is peptide-bonded of lysine. It is manufactured by chemical synthesis. It is also manufactured small amount of scale as a reagent and is not manufactured as an industrial scale.
ε-Polylysine is linear structure, whereas α-Polylysine forms secondary structures such as α-helices like normal proteins. And 4-aminobutyl lysine side chains are attached to its main chain.
Because it is made by chemical synthesis, it is difficult to control the molecular weight, and it is characterized by a wide molecular weight distribution. α-Polylysine is also sold DL racemic α-Polylysine. Currently, it is mainly used at the reagent as a cationic polymer. For example, it is used as a coating agent for culture vessels to improve the adhesion of cultured cells. But, there is a report that ε-Polylysine shows higher cell adhesiveness in some cells comparison for α-Polylysine. It is speculated that this is due to the difference in the structure of the α- and ε-forms.
α-Polylysine is registered with INCI (International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients) under the name “POLYLYSINE”. On the other hand, ε-Polylysine is registered with INCI under the name “POLYEPSILON-LYSINE”. In China's Cosmetic Ingredients Catalog (IECIC), α-Polylysine is registered as a raw material with reference to POLYSINE. On the other hand, ε-Polylysine is not registered in IECIC.
Table. Summary of various Polylysines
| ε-Polylysine | ε-Polylysine hydrochloride | α-Polylysine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| INCI名 | POLYEPSILON-LYSINE | - | POLYLYSINE |
| IECIC | - | - | POLYLYSINE 聚赖氨酸 |
| Structure |  |
 |
 |
| Chemical synthesis process | None | Salt forming reaction | All process |
| Food additive | JP, KR, CN | CN | None |
| Remarks | JNC’s Polylysine has FDA GRAS. (GRN No.135 and 336) |


