CellufineTMGCL-2000HF
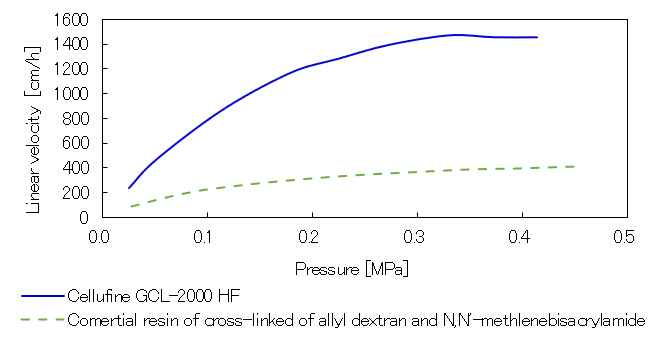
Size exclusion chromatography is a separation mode that separates proteins by the difference in molecular weight. In principle, it is necessary to reduce the particle size to improve the separation performance. Therefore it causes difficulty of operating high flow rate because of its pressure loss. This feature of size exclusion chromatography is a bottleneck in process design. Cellufine GCL-2000HF was developed to eliminate this bottleneck. Since it is based on spherical cross-linked cellulose particles, it has high physical strength and can be operated at high flow rate, so it can be used on an industrial scale. In addition, it has a pore size optimized for protein separation, so it exhibits excellent separation performance.
Features
- Rigid spherical particles
- Outstanding mechanical strength
- Hydrophilic
- High pore volume
- Broad selection of fractionation range
- Supplied preswollen
- High chemical resistance
- Autoclavable at 121 °C for 30 minutes
Benefit
- High flow rate compatibility even in large diameter process columns
- May be pumped or stirred without fines generation
- Low non-specific adsorption and high recovery
- Good capacity
- Optimize selectivity to required molecular weight range
- No time-consuming swelling procedures required
- Usable with all common salts, detergents, chaotropic agents, organic solvents
- Depyrogenation
- Sterilizable
- Regulatory Support
| Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Matrix | Cross linked cellulose |
| Particle Shape | Spherical |
| Particle Size | ca. 40-130 μm |
| Chemical Resistance | Media can be used with most salts, detergents, solvents, acids and bases, including 8M urea, 6M guanidine / HCL, 0.1M HCL and 0.5M NaOH |
| Mechanical Resistance | Media will withstand peristaltic pumping and extended magnetic stirring |
| Schrinkage / Swelling | Shrinkage or swelling < 3 % with changes in pH or ionic strength. Shrinkage or swelling with solvents varies with solvent and media |
| Autoclavable | 121 °C for 30 minutes |
| Supplied | Suspension in 20 % ethanol |
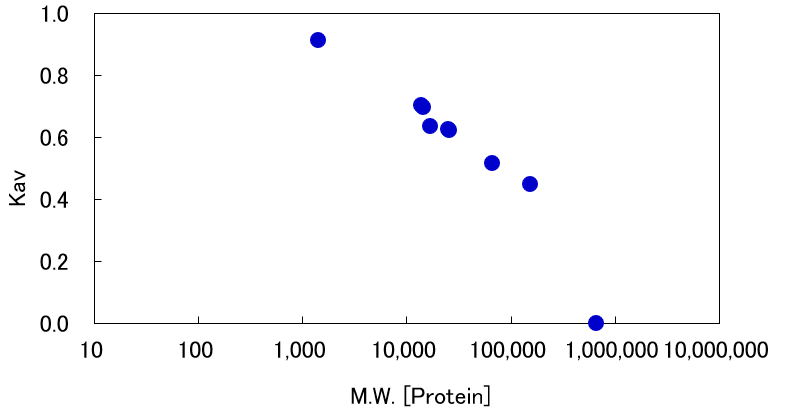
Range of Fractionalization
Cellufine GCL-2000HF can be separating proteins with a wide range of molecular weight. Figure 1 and Table 1 show the results of measuring the exclusion limit of GCL-2000HF.
| Protein | MW | Kav |
|---|---|---|
| Thyrogloburin | 660,000 | 0.00 |
| IgG | 155,000 | 0.45 |
| BSA | 66,000 | 0.52 |
| Chymotrypsinogen A | 25,700 | 0.62 |
| α-Chymotrypsin | 25,200 | 0.62 |
| Myoglbin | 17,000 | 0.63 |
| Lysozyme | 14,300 | 0.70 |
| Ribonuclease A | 13,700 | 0.70 |
| Bacitracin | 1,400 | 0.91 |
Table 1 Relationship between proteins and Kav
Proteins of different molecular weights were loaded into a column packed Cellufine GCL-2000HF. Kav was measured based on the amount of volume eluted from the column.
Pressure Flow Curves
Protein Recovery
| Protein | % Recovery |
|---|---|
| Catalase | 100 |
| lgG | 100 |
| Aldolase | 100 |
| Serum Albumin | 100 |
| Lactoglobulin | 100 |
| Ribonuclease | 100 |
| Cytochrome C | 100 |
| Lysozyme | 100 |
| Chymotrypsinogen A | 99 |
| Myoglobin | 97 |
Excellent stability (accelerated test)
Cellufine GCL-2000HF is a size exclusion chromatography resin cross-linked with cellulose particles that are extremely stable as a substance.
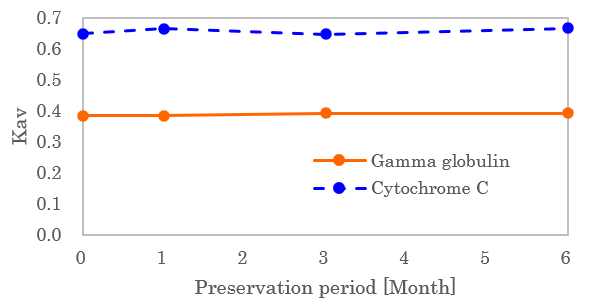
Cellulose is a heat-stable polysaccharide. The agarose, which is commonly used as a chromatography resin, has many hydroxyl groups because it is the same polysaccharide as cellulose. Therefore, like cellulose, it has the characteristic of less non-specific adsorption of proteins. On the other hand, agarose is easily dissolved in hot water. For this reason, agarose has the disadvantage of being sensitive to heat. Although cellulose is a polysaccharide with hydroxyl groups, it has an extremely excellent feature of resistance for heat because of crystalline structure in it.
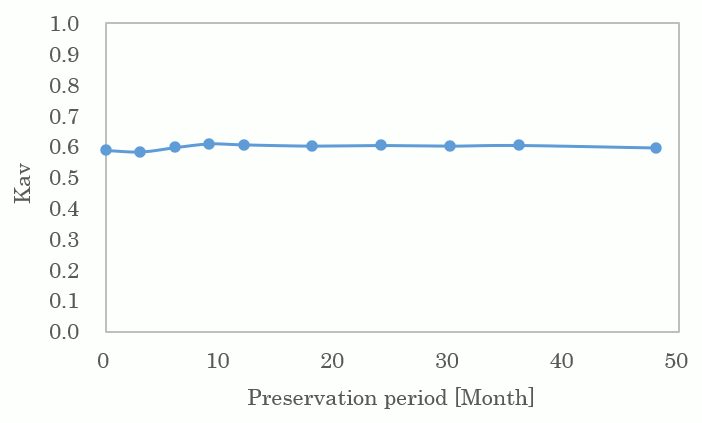
Excellent stability (preservation test)
Cellufine GCL-2000HF was stored at a temperature of 30 ° C in a 20% ethanol solution, and the subsequent changes in pore size were investigated (Fig. 4). It was found that Cellufine GCL-2000HF shows excellent stability over a long period.
- Cellufine GCL-2000HF
