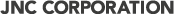Aerobic bacteria count
| Interpretation | Aerobic bacteria form red colonies, these all colonies are aerobic bacteria. If more than 300 colonies are formed, which is the upper limit of the counting range, accurate measurements will be difficult. Dilute the sample to fit within tne counting range. In this case, total number of colonies can be estimated by multiplying 20 folds of counting colonies in a 1×1 grid. Use this as a reference to optimize the dilution ratio. |
|---|
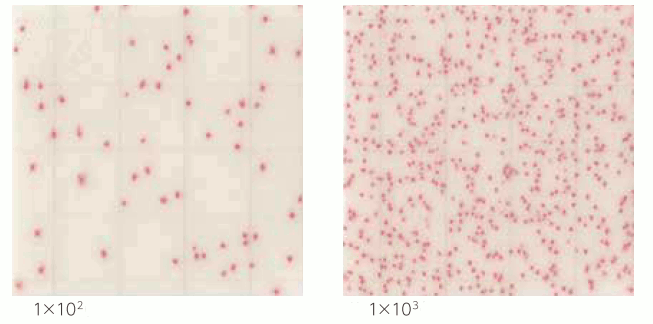
Aerobic bacteria count
| Interpretation | If the number of colonies is 104 or more, the entire medium tends to turn red and counting will be difficult. Optimize the dilution ratio. |
|---|
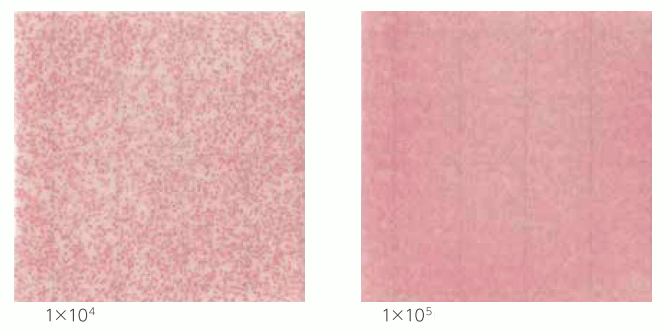
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacillus
| Interpretation | Highly motility microorganisms such as Bacillus may form spreading red colonies. The spreading colony should be counted as one colony. |
|---|
Gram-negative bacteria
| Interpretation | Gram-negative bacteria form red colonies similarly to gram-positive bacteria. For this reason, it is not possible to distinguish between gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. |
|---|
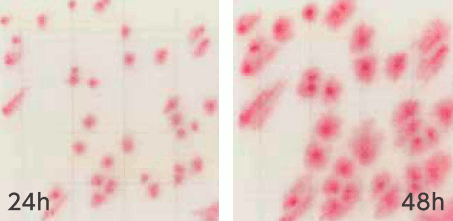
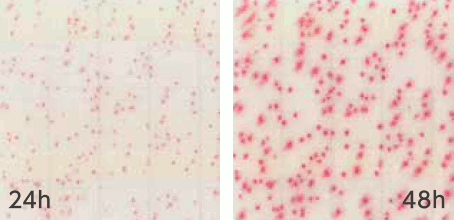
Lactic acid bacteria

| Interpretation | Although red colonies can be observed even after 24-hour culture, 48-hour culture is recommended for accurate counting. |
|---|
Cold bacteria

| Interpretation | Although red colonies can be observed even after 24-hour culture, 48-hour culture is recommended for accurate counting. |
|---|
Food sample
Parsley
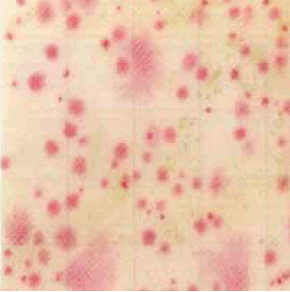
| Interpretation | Although food-derived pigments remain on the surface of the pad, only count red colonies. Color may remain not only in parsley but also in dark pigmented specimens. If the color is dark and difficult to count, dilute it. If the number of bacteria is small when the dilution is 100 folds, adjust the dilution ratio appropriately, such as 50 folds. |
|---|
Food sample
Hijiki (Japanese food)

| Interpretation | There is food residue, but the color is different, so colony counting is possible. In addition, if there is red food residue, it can be counted because the color and shape derived from microorganisms are different. The part surrounded by red is the colony. |
|---|
Food sample
Cream cheese

| Interpretation | Radial colonies are more likely to be mold. You can see that the hyphae are spreading. Depending on the type of mold, colors such as black and blue may be mixed in the red colony. This is because the mold forms spores, which causes the pigments to overlap in color. |
|---|
Food sample
Pineapple
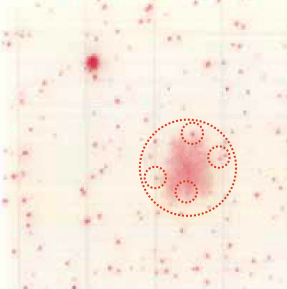
| Interpretation | This is an example of both small colonies and large spread colonies. Largely spread colonies are also counted as one. Colonies in the spread colonies are also counted. |
|---|
Food sample
Raw walnuts
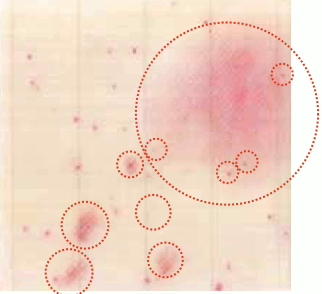
| Interpretation | There are colonies that spread widely and colonies that spread in a flowing manner, but since there is a core near the center of color development, it is counted as one colony. |
|---|